
If you are looking for how to invest in crypto assets you are in thre right place. I tried to prepare a real guideline that will guide you trought the world of crypto assets, investments and technology. The good news is that this is no magic formula, juts method and a good due dilligenge. The bad news is that the technology is moving so fast that is hard to keep and even conceptualize some of more advance cryptographic concepts. But don’t worry and most of all don’t FOMO .
The idea of this article is to cover everything, starting with basic technology concepts and ending from an Investor perspective.
So: What is the best cryptocurrency to invest in? How to choose and analyze a Cryptocurrency? Here you can learn how to do it and win with the market.
First Steps
If you are not a complete noob in crypto please jump this part where i´m going to explain what´s the diference between the existing assets on the market and i´ll try to clarify some base concepts.
Web 3.0, Cryptography and Blockchain
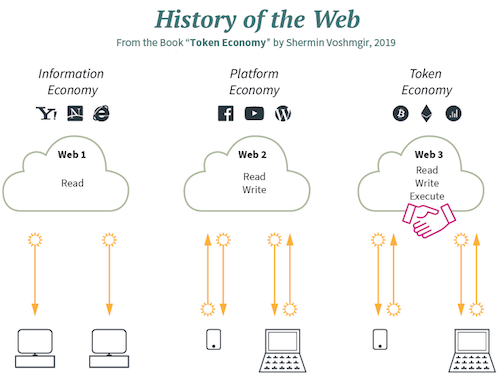
The World Wide Web (www) has changed the world and the way we interact with information forever and has drived a revolution in social interactions and (e-)commerce. But there are some issues. An Overload of data is stored in servers and at the meantime users, that are the central players of this interactions, keep leaving their data in every website without knowing how its going to be used. The question that arises is: do we trust this entities to “guard” or data?
Web 2.0 was a frontend revolution that made all the internet much more usable and fast for all of us, but at the same time created a bunch of privacy problems, where the Cambridge Analytics was the most visible scandal around it. Failing clearly with one of a their biggest claims: a descentralized world. Insteád the Internet is ruled by a few companies that control all the information flux.
Web 3.0 is here with the promise of solving lots of this issues. The internet we use today doesn’t have the a native mechanism to transfer what computer science refer to as “state” – the status of who is who, who owns what and who has the right to do what. While web2.0 was a frontend revolution the web3.0 is happenning without the must of us notice at the backend of the web.
State is crucial for managing values and the ability to transfer value form one entity or person to another. if you cant hold sate in the internet you will need to trust a centralized entity to transfer value for you with the limitations on their will to do that. The simplicity of the tcp/ip, smtp or http protocols regulates how the transmission of information is done but no how data is stored.
The Web3.0 claims that P2P (peer to peer) is the future of the internet. A more clever and user privacy friendly internet. No midleman, you own your data.
Cryptography is the pratice and study of secure communication in the presence of a validator 3rd party. The objective is to create informations systems that are resilient against eavesdropping, manipulation and other forms of attack. You can have a bigger picture of cryptography’s history and concept here. The basic concept implies that person A can send information to person B and only that person can read that information even if ther are other person involved in the transaction.
When applied to blockchain the main goal is to identify all network actors without compromising their privacy. While, im not going to enter in too much technical details, there are some basic concepts that are very important to retain:
- A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values. The values returned by a hash function are called hash values, hash codes, digests, or simply hashes. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a hash table. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called hashing or scatter storage addressing
- Symmetric-key algorithms[a] are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both the encryption of plaintext and the decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical, or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys.[1] The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link.[2] The requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric-key encryption, in comparison to public-key encryption (also known as asymmetric-key encryption)
- Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public-key cryptography, is a process that uses a pair of related keys — one public key and one private key — to encrypt and decrypt a message and protect it from unauthorized access or use. This is the model that is used in most blockchain projects

The main purpose of using public key cryptography for the bitcoin blockchain is to create a secure digital reference about the identity of the user.
Wallets & Keys
A blockchain wallet is a piece of software that stores your private key, public key and blockchain adress. Be aware since the beginning that different tokens or cryptocurrencies may run on different blockchains, for instance if you want to send some asset on Etherium network using and dex (descentralized exchange) you must be sure that the token and the wallet are compatible.
Your wallet is the key. Or the keys. Usually it has a password plus a recover pass with 12 separated words that you must guard with your life, afterall you may choose to keep part of yout cryptos in there. Metamask( it supports several blockchains), Coinbasewallet are two examples of software wallets. You have as well hardwallets that are wallets as a device beeing Ledger the most know one.
The Blockchain
The concept of blockchain first come in 2008, as part of the proposal of Bitcoin with the objective of creating P2P money without banks. The promise was to solve the trust-existing problem between human interactions and the biggest claim of this brand new technology was to make possible a payment flow or simple database validation to run without a central authority and where the participants do not need to trust or even know each other. If you think of the number of regulations, jurisdictions, countries worldwide and the bureaucracy associated with money, propriety and services transference in a global scenario you may be starting to understand the game changer this technology could be.
The Blockchain provides a universal state layer that is at the same timer a data set that every actor can trust and that cannot be changed (in theory). Although the blockchain and P2P academic discussion has begun in the 80´s only since 200 was possible to start to think in practical applications of this kind of technology.
Actually blockchain has solved since the very begin a very important Internet issue: The Double-Spending (Internet) problem – AKA: i can make infinite copies of a file! How did it solve it? By making very very expensive to make replicas of digital values – the same principle for what central banks already do with bills and coins. The concept of Distributed Ledger where the data is immutable by and 3rd party entity and there is a copy of the ledger stored in several devices of a cryptographically secured P2P network. The Ledger is also a file called blockchain that maintains in permanency an increasing number of transaction data records, chained in blocks that are protected by cryptography.
Distributed Ledger: The Bitcoin Blockchain Protocol introduced a mechanism that makes very very expensive to copy digital values. A Copy of the ledger is stored on multiple places inside a P2P Network. The Ledger File is called blockchain! Different people and companies that dont trust each other can now share information without requiring a central administrator. This ledger is like a spreadsheet with all the transactions ever made and in order to change consensus between several independent validators is needed. It cant be changed backwards. anyone can see what happens on the chain but no single user can change it.
Proof of Work – Decentralized cryptocurrency networks need to make sure that nobody spends the same money twice without a central authority like a central bank in the middle. To accomplish this, networks use something called a “consensus mechanism,” which is a system that allows all the computers in a crypto network to agree about which transactions are legitimate.
There are two major consensus mechanisms used by most cryptocurrencies today. Proof of work is the older of the two, used by Bitcoin, Ethereum 1.0, and many others. The newer consensus mechanism is called proof of stake, and it powers Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, Tezos and other (generally newer) cryptocurrencies. To understand proof of stake, it’s helpful to first understand proof of work, so we’ve paired them in this explainer.
Some characteristics of Blockchain(and Bitcoin):
- Shared
- Public
- Ledger of Transactions
- Anyone can Inspect the transactions
- No single entity controls the ledger
Why is it so expensive to manipulate a Blockchain transaction ( and why it makes the blockchain safer)
A Blockchain network stores all the information in a cryptographically secured data pieces called blocks. The first block in a blockchain is called the Genesis block. Each block has limited storage size. Blocks store the information about previous block and they are chained together and they are encrypted. Each new block(containing transactions) is added to the to the blockchain by consensus of the network (whatever the consensus mode is). Lets say that the “network” is working on the block 100 of the chain but somebody on the network (node) wants wants to manipulate a transaction in block 89. The Node/person that wants to make this change in the block 89 have to re-do all the transactions on the blocks 89 until 99. Thats 11 blocks of very very expensive computing power (millions!) and he has to do this before the network is done with block 100.
Types of Blockchains
Although the idea of Blockchain gained prominence and fame after the launch of Bitcoin in 2008, the idea was conceived in 1991, when Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta with their work on cryptographically secure (tamper-proof) data blockchain and timestamps associated, gained prominence and brought this concept to the world. But there is a subtle difference between Digital Ledger Technologies (DLTs) and blockchains. Although it is still an unfinished debate, one of the most relevant differences is in the types of consensus of both technologies.
From a theoretical point of view, DLT is a broader term used to encompass digital database technology that has different implementations, Blockchain being the most popular. DLT technology consists of nodes in the underlying network that employ different processes to reach a common conclusion, according to Stornetta. Thus, DLT technology not only digitized an entire database, but provided the features of dynamism, immutability, security, and decentralization to it.
Basically, blockchains are consensus mechanisms, where all participants of the nodes verify whether or not a transaction has occurred, before storing the transaction value and the digital signatures of the sender and recipient. A final step before storing the information in the block is to assign the data code that also contains the information from the predecessor block, thus maintaining the blockchain. Depending on the types of blockchain, other people may or may not see the transactions.
The most popular blockchains are related to cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. This type of blockchain has the disadvantage of transaction per second (TPS) limitations or the lack of scalability, which gives miners the power to delay or cancel the transaction completely. For this there are the consensus mechanisms that limit such power to the miners.
The consensus mechanism, related to the validation of transactions being added to the DLT/blockchain, requires consensus to be reached before the ledger is updated to ensure that only legitimate transactions are recorded in the chain. The consensus mechanisms are decentralized, meaning that no single authority is responsible for changing the state of the network.
Types of consensus mechanisms
- Proof-of-Work – Bitcoin e Litecoin
- Proof-of-Stake – Ethereum
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) – Utilizado nos projetos Bitshares, Steemit, EOS e Lisk
- Leased Proof-of-Stake
- Transactions as Proof-of-Stake
- Proof-of-Importance
- Proof-of-Capacity
- Proof-of-Weight
- Proof-of-Authority
- Proof-of-Elapsed-Time
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- Federated Byzantine Agreements – Utilizado na Stellar e Ripple
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance
- dBFT (Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance) – Utilizado no projeto NEO
- Hashgraph (asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance, Gossip Protocol, Virtual Voting)
Real Life Crypto Projects
In Theory the advantages of decentralisation seem obvious, but what looks like good in theory may not be in pratice.
There are several cryptocurrency projects that have real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
- Ethereum: Ethereum is a decentralized platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). These can be used in a variety of industries, such as supply chain management, voting systems, and digital identity.
- IOTA: IOTA is a cryptocurrency designed for the Internet of Things (IoT). It aims to facilitate secure and efficient communication and transactions between connected devices.
- Ripple: Ripple is a real-time gross settlement system, currency exchange, and remittance network. It is designed to enable fast and inexpensive cross-border transactions for financial institutions.
- Stellar: Stellar is an open-source, decentralized protocol for digital currency to fiat money transfers which allows cross-border transactions between any pair of currencies.
- Blockstack: Blockstack is a decentralized computing network and app ecosystem that allows users to own their data and maintain control over their digital identity.
- Solana: Solana is a high-performance blockchain protocol that allows users to build decentralized apps and run them at scale. It aims to provide a fast and efficient infrastructure for decentralized finance (DeFi) and other blockchain-based applications.
- Please note that these are only examples and the list is non-exhaustive.
Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. It is a digital contract that can be programmed to automatically execute the terms of the agreement once certain conditions are met. Smart contracts allow for the automation of a wide range of processes, including the exchange of money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent and conflict-free way.
Smart contracts are built on blockchain technology, which provides a decentralized and tamper-proof way to store and execute the contract. This allows for the execution of the contract to be trustless and autonomous, as it does not require any intermediaries such as lawyers or banks to enforce the terms of the contract.
Some examples of smart contract usage can be found in supply chain management, voting systems, digital identity, insurance, and in decentralized finance (DeFi) to name a few.
Self-enforcing agreements, also known as “smart contracts,” are agreements that are encoded into computer programs and executed automatically by a computer when certain conditions are met. These agreements are self-executing, meaning they do not require human intervention to enforce their terms.
Self-enforcing agreements are based on the idea that the terms of a contract can be encoded into a computer program, making it possible for the program to automatically execute the terms of the agreement without the need for intermediaries such as lawyers or banks. This is possible because the code of a smart contract can be set up to automatically check the conditions of the agreement and execute the terms of the contract when those conditions are met.
For example, a self-enforcing agreement could be used in a supply chain management system to automatically release payment to a supplier when a shipment of goods is received and verified. Or in the case of decentralized finance (DeFi) to execute trades, loans or other financial transactions automatically on the blockchain network.
The use of smart contracts can increase transparency, efficiency, and security in agreements, and has the potential to revolutionize many industries.
DAOS – Instituitional Economics of Tokenizes Networks
DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) are a new type of organization that is run by code, rather than people. These organizations use smart contracts and tokenized networks to operate, making them decentralized and autonomous. They operate based on the consensus of their token holders, who have the power to vote on proposals and make decisions for the organization.
DAOs are powered by tokenized networks, such as blockchain, which provide the infrastructure for them to operate. The use of smart contracts on a blockchain network allows for the transparent and secure management of assets, and for the execution of the organization’s rules and decisions in a trustless manner. The decentralized nature of DAOs allows for new types of organizations to form, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms or decentralized marketplaces.
The use of smart contracts in DAOs allows for the automation of many processes, from the management of assets to the voting process. This can increase efficiency and transparency, and reduce the need for intermediaries such as lawyers or banks to enforce the terms of the agreement.
One of the main advantages of DAOs is the decentralization of decision making. This allows for a more democratic and fair decision-making process, where all token holders have a say in the direction of the organization. This also opens opportunities for new types of organizations to form, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms or decentralized marketplaces.
The use of tokenized networks in DAOs also provides security and transparency, as all transactions and assets are recorded on a tamper-proof ledger. The use of tokens also allows for the easy transfer and management of assets, as they can be easily bought, sold, and traded on a tokenized network.
In conclusion, DAOs and tokenized networks are ushering in a new era of decentralized and autonomous organizations that have the potential to revolutionize industries. With their ability to automate processes, decentralize decision making, and provide security and transparency, DAOs and tokenized networks have the potential to disrupt traditional business models and create new opportunities for innovation.
The Future of Money
The future of money and blockchain technology are closely intertwined. Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we conduct financial transactions, by providing a decentralized and secure platform for digital transactions. This means that there would be no need for intermediaries such as banks, making transactions faster, cheaper, and more secure.
One of the most promising applications of blockchain technology is the development of digital currencies. Bitcoin, the first decentralized digital currency, was created in 2009 using blockchain technology. Since then, many other digital currencies have been created, and their use is becoming more widespread. Digital currencies offer many advantages over traditional fiat currencies, including faster and cheaper transactions, and the ability to conduct transactions on a global scale.
Another area where blockchain technology is likely to have a significant impact is in the area of supply chain management. By using blockchain, companies can create a transparent and secure record of all transactions, from the point of origin to the point of consumption. This can help to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of fraud.
In the future, we can also expect to see blockchain technology being used in other areas such as voting systems, smart contracts, and digital identity management. These applications have the potential to create more secure and efficient systems, with the added benefit of being able to reduce costs and increase transparency.
Overall, the future of money and blockchain technology is very promising. As the technology continues to evolve and become more widely adopted, we can expect to see significant changes in the way we conduct financial transactions, and the way in which we interact with digital assets. It’s important to note that along with the potential benefits, there are also some risks, such as scalability, regulatory, and legal challenges that will need to be addressed. Nonetheless, the future of money and blockchain technology is worth exploring and investing in.